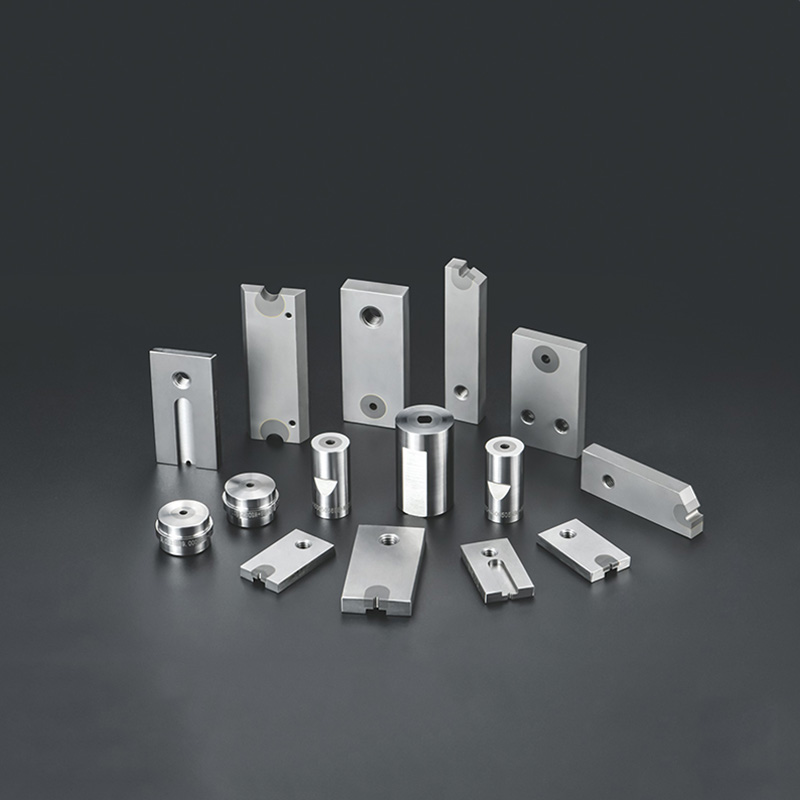
In the manufacturing of fasteners, particularly bolts, bolt dies play a crucial role in ensuring precision, durability, and consistent quality. Bolt dies are specialized tools used to shape, cut, and thread bolts during the manufacturing process, creating fasteners that meet industry standards and specific application needs. This article explores the importance of bolt dies, their manufacturing process, the types of dies used for bolt production, and their applications across various industries.

1. What Are Bolt Dies?
Bolt dies are precision-engineered tools designed to form and shape bolts, particularly the threaded portion, which is essential for the bolt’s function. In the manufacturing of bolts, dies are used in processes like Cold Heading, threading, and trimming to create the head and threads of the bolt. These dies are typically made from high-strength materials such as tool steel or Tungsten Carbide, ensuring they can withstand the pressures and wear of mass production.
The quality of the bolt die directly influences the quality of the bolts produced. High-precision bolt dies result in accurate, durable fasteners that can meet the specific requirements of various industries, from automotive and aerospace to construction and electronics.
2. Types of Bolt Dies
There are several types of dies used in the bolt manufacturing process, each serving a specific function. The two primary categories of dies used in bolt production are:
Heading Dies: These dies are used during the cold heading process to form the head of the bolt. Cold heading involves shaping the head of the bolt by striking a metal blank into the desired form without heating it. The heading die ensures the bolt head is shaped according to design specifications, whether it is a hexagonal, round, or other shaped head.
Threading Dies: Threading dies are used to cut or form the threads along the shaft of the bolt. They are typically designed with high precision to create the correct pitch, depth, and angle of the threads. Thread rolling dies, a subtype of threading dies, are used to cold-form the threads rather than cut them, producing stronger and more wear-resistant threads.
In addition to these, trimming dies are sometimes used to remove excess material or refine the shape of the bolt after it has been headed and threaded.
3. Manufacturing Process of Bolt Dies
The process of creating bolt dies involves several steps to ensure that the dies can withstand the demands of production while maintaining precision:
Design and CAD Modeling: The first step in producing a bolt die is designing it based on the specifications of the bolt. This includes determining the size, shape, thread type, and other necessary characteristics. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is used to create detailed models of the die before production.
Material Selection: The material used to make bolt dies must be highly durable, wear-resistant, and able to withstand repeated use under high pressure. Tool steels and Tungsten Carbide are commonly used for bolt dies due to their hardness and resistance to wear.
CNC Machining: The die is produced using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining. This method ensures the highest precision in forming the intricate features of the die, such as the thread profiles and head shapes. CNC machining allows for tight tolerances, which are critical in ensuring that the bolts produced meet exact specifications.
Heat Treatment: After machining, bolt dies are typically heat-treated to improve their hardness and durability. This process enhances the wear resistance of the die, ensuring a longer tool life and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Polishing and Surface Finishing: Finally, the bolt dies are polished and finished to ensure smooth surfaces, reducing friction during the forming process and improving the quality of the finished bolts.
4. Advantages of Using High-Quality Bolt Dies
Investing in high-quality bolt dies offers several significant advantages for manufacturers:
Precision and Consistency: Quality bolt dies produce bolts that meet precise specifications, ensuring consistency across large production runs. This is particularly important for industries like automotive and aerospace, where the quality of fasteners is critical for safety and performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance: High-quality bolt dies, particularly those made from materials like Tungsten Carbide, offer excellent durability and resistance to wear. This reduces the frequency of die replacements and maintenance, resulting in higher production efficiency.
Enhanced Production Efficiency: By using well-designed dies, manufacturers can increase production speeds without sacrificing quality. Dies that are optimized for fast, efficient production processes help reduce costs and improve overall manufacturing throughput.
Improved Bolt Strength: Thread rolling dies, in particular, offer an advantage in terms of bolt strength. Rather than cutting the threads, which can weaken the material, thread rolling forms the threads through cold working, resulting in stronger, more durable threads.
5. Applications of Bolt Dies
Bolt dies are used in a wide range of industries, each with its own specific requirements for bolt design, strength, and performance. Some of the key applications include:
Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, bolts are used in critical components such as engines, transmissions, and suspension systems. The bolts must be able to withstand high levels of stress and vibration, making the precision and durability of the dies used to create them essential.
Aerospace Industry: Aerospace bolts must meet stringent safety and performance standards, as they are used in aircraft structures and engines. High-quality bolt dies ensure that the fasteners produced are reliable, safe, and capable of withstanding extreme conditions.
Construction Industry: In construction, bolts are used to secure structural elements, machinery, and equipment. The bolts must be strong and resistant to corrosion, making the precision of the threading and the material properties of the dies critical.
Electronics and Electrical Industries: Precision bolts are often required in electronics and electrical applications, where they are used to assemble sensitive components. The high accuracy of the bolt dies ensures that the fasteners meet the specific size and tolerance requirements for these delicate assemblies.
6. Maintenance and Care of Bolt Dies
To ensure that bolt dies continue to function effectively over time, regular maintenance and care are essential. Proper storage, cleaning, and lubrication of the dies can help extend their life and maintain production quality. Additionally, periodic inspection of the dies for signs of wear or damage can prevent costly production delays or defects in the bolts being produced.
Bolt dies are essential tools in the fastener manufacturing process, ensuring that bolts are produced with the precision, strength, and durability required by various industries. By investing in high-quality dies made from durable materials like tungsten carbide and tool steel, manufacturers can improve their production efficiency, reduce downtime, and produce bolts that meet the demanding specifications of modern engineering and construction projects. As industries continue to evolve and require even more reliable fasteners, the importance of well-crafted bolt dies will only increase, cementing their place as a cornerstone of high-quality manufacturing.