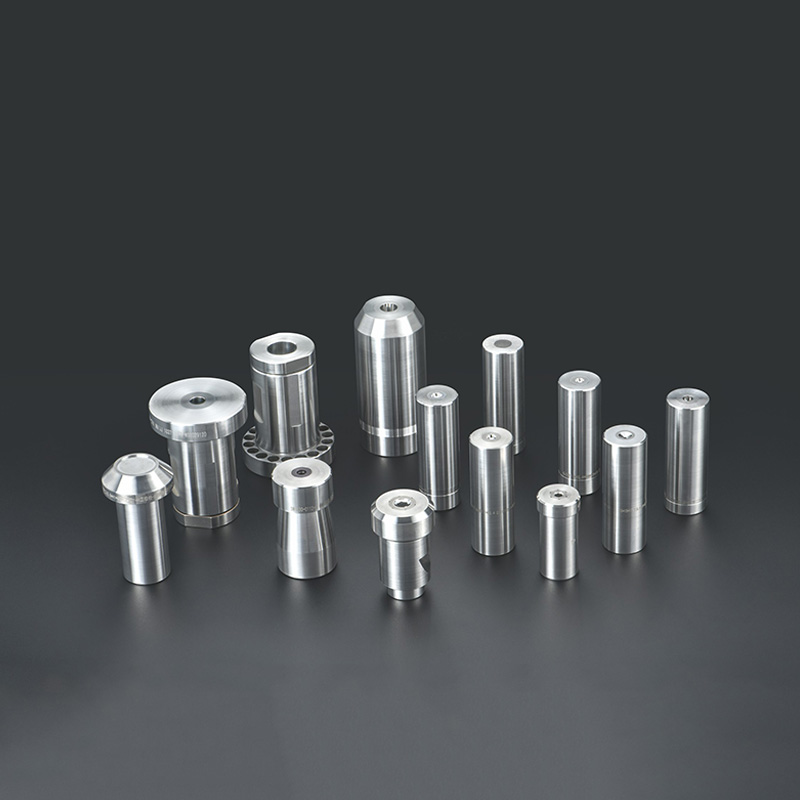
Cold Heading Dies play a critical role in manufacturing processes, especially in the production of fasteners like bolts, nuts, and rivets. These tools are subjected to immense pressure and wear, making proper maintenance and care essential to ensure their longevity and optimal performance. In this article, we’ll explore practical tips for cleaning, lubricating, and storing Cold Heading Dies to maximize their service life.

The Importance of Proper Maintenance
Cold Heading Dies are precision tools made from high-strength materials like high-speed steel or Tungsten Carbide. Despite their robustness, continuous exposure to extreme stress and heat during operation can lead to wear and tear. Proper maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the dies but also ensures consistent product quality and minimizes downtime in production.
Cleaning: Removing Contaminants for Better Performance
After each use, cold heading dies must be thoroughly cleaned to remove debris, metal shavings, and residual lubricants. These contaminants can cause abrasion, corrosion, and dimensional inaccuracies if left unaddressed.
Cleaning Tips:
1.Ultrasonic Cleaning: For intricate die shapes, ultrasonic cleaning effectively removes fine particles lodged in small crevices.
2.Chemical Cleaning Solutions: Use non-corrosive solutions to dissolve grease and other residues without damaging the die surface.
3.Manual Cleaning: Employ soft brushes and lint-free cloths to wipe down surfaces, avoiding harsh abrasives that could scratch the die.
Lubrication: Reducing Friction and Wear
Lubrication is crucial for preventing friction and reducing the heat generated during cold heading operations. Proper lubrication minimizes surface wear, protects against rust, and ensures smooth functionality.
Lubrication Guidelines:
1.Select the Right Lubricant: Choose high-performance lubricants designed for extreme pressure and high-temperature conditions.
2.Regular Application: Apply lubricant consistently, ensuring even coverage across working surfaces.
3.Inspect Lubricant Condition: Over time, lubricants can degrade and lose effectiveness. Replace them regularly to maintain protection.
Storage: Preventing Corrosion and Physical Damage
When not in use, cold heading dies must be stored in a manner that prevents exposure to environmental elements and physical damage. Improper storage can lead to rust, pitting, or deformation, all of which compromise die functionality.
Storage Best Practices:
1.Dry and Cool Environment: Store dies in a humidity-controlled area to prevent corrosion. Use desiccant packs if necessary.
2.Protective Coatings: Apply rust-preventive coatings before storage to shield the dies from moisture.
3.Dedicated Storage Units: Keep dies in individual compartments or cases lined with soft materials to avoid scratches and impact damage.
Proactive Maintenance: Scheduled Inspections and Repairs
In addition to daily care routines, schedule regular inspections to detect early signs of wear or damage. Utilize precision measurement tools to ensure that dies meet required dimensional tolerances. Address minor issues immediately to prevent costly failures during production.
Effective maintenance of cold heading dies is not just a cost-saving measure but also a strategy for ensuring consistent manufacturing quality. By adopting proper cleaning, lubrication, and storage practices, manufacturers can significantly enhance die longevity and production efficiency.
Investing time in proactive maintenance will pay dividends by reducing downtime, improving output, and extending the service life of these indispensable tools. Start implementing these tips today to maximize the value of your cold heading dies.