What are Trimming Dies?
Trimming Dies are precision tooling components used in manufacturing processes to remove excess material (flash or burrs) from molded, forged, or stamped parts. These dies achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm for high-precision applications and typically operate at forces ranging from 5 to 200 tons, depending on material hardness and part geometry.
Key characteristics of modern Trimming Dies include:
Material Composition: Typically made from tool steels like D2 (HRC 58-62) or carbide inserts for wear resistance
Clearance Angles: Optimized between 5-15% of material thickness to minimize burr formation
Surface Finish: Ground to Ra 0.2-0.4 μm for smooth cutting edges
Thermal Stability: Maintain dimensional accuracy within 0.01 mm/m°C during operation
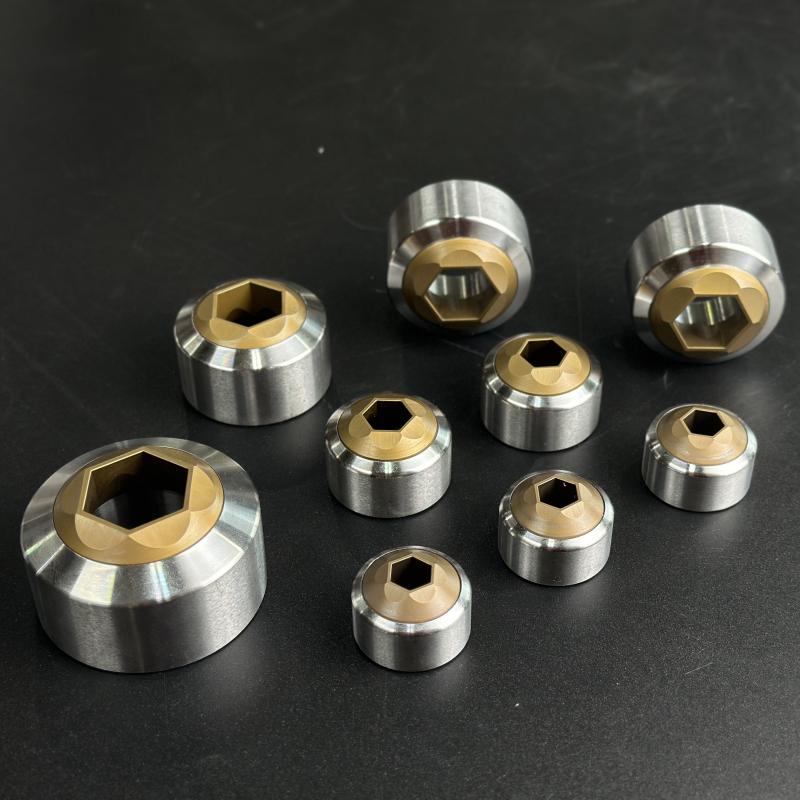

Application Scenarios
Trimming Dies serve critical functions across multiple industries:
1. Automotive Manufacturing
Used for precision trimming of stamped body panels with cycle times as fast as 12-15 strokes per minute. Typical applications include:
Door panel flash removal (aluminum alloys, 1.0-2.5mm thickness)
Bumper bracket trimming (high-strength steels up to 1500 MPa)
2. Aerospace Components
For titanium and composite parts requiring ±0.025 mm positional accuracy:
Turbine blade root form trimming
Composite layup edge finishing
3. Consumer Electronics
Micro-trimming of magnesium alloy casings with feature sizes down to 0.3 mm:
Smartphone chassis deburring
Laptop hinge component finishing
4. Medical Device Production
Ultra-precision trimming of implantable components:
Stainless steel orthopedic implants (316L, 17-4PH)
Polymer catheter tip forming
Maintenance Procedures
Proper maintenance ensures trimming dies achieve their typical service life of 500,000-2,000,000 cycles:
Daily Maintenance
Inspect cutting edges for chipping (use 10x magnification)
Clean die surfaces with non-chlorinated solvents
Verify guide post lubrication (ISO VG 68 oil)
Weekly Procedures
Measure punch/die clearance with feeler gauges (maintain within 5-8% of material thickness)
Check spring pressures (deviation ≤ 10% from spec)
Inspect scrap removal systems
Monthly Maintenance
Perform hardness testing (Rockwell C scale) on critical edges
Check parallelism of die shoes (≤ 0.02 mm/m)
Reapply anti-galling coatings (e.g., TiN, CrN)
Sharpening Techniques
When edge radius exceeds 0.05 mm:
Use CNC tool grinders with 46-80 grit CBN wheels
Maintain original rake angles (± 0.5°)
Limit material removal to 0.02-0.05 mm per sharpening
Critical maintenance data points:
Die temperature during operation should not exceed 120°C
Punch deflection must remain below 0.001 x die opening length
Lubricant viscosity should be maintained at 40-70 cSt at operating temperature