A Cold Forging Die is a manufacturing tool used to shape metal blanks at room temperature to produce a variety of parts. It usually consists of mold cavity, punch, guide system and ejector pin. The cold forging mold is simple to operate, can quickly achieve forming, and does not require additional heating equipment, thus saving energy and time costs. Because they are formed at room temperature, Cold Forging Dies avoid deformation and damage caused by overheating of the material, allowing the production of high-quality, high-precision parts. Cold forging molds are widely used in automobile, electronics, aerospace and other industries, providing important technical support and production solutions for the manufacturing industry.
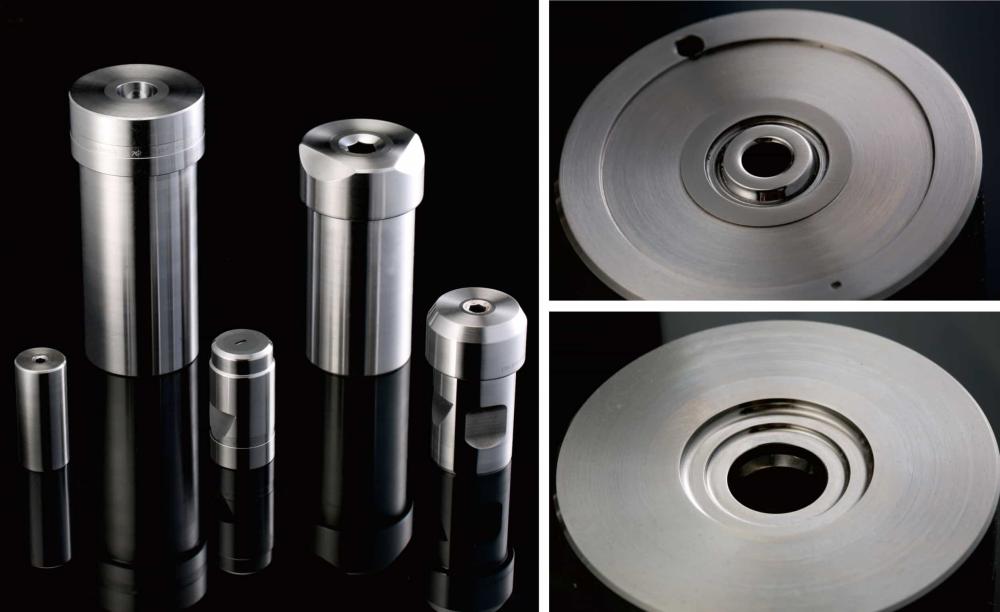

Key Features
1.Material Composition:Cold Forging Dies are typically made from high-grade tool steels such as H13, SKD61, or carbide, known for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. These materials ensure the dies can withstand the intense pressures involved in the forging process.
2.Precision Engineering:Cold Forging Dies are engineered with high precision to produce parts with tight tolerances and complex geometries. The dies are often designed using advanced CAD/CAM software, ensuring that every detail is meticulously planned and executed.
3.Surface Treatment:To enhance the durability and lifespan of the dies, various surface treatments are applied, such as nitriding, PVD coating, or carburizing. These treatments increase the surface hardness and resistance to wear and corrosion, allowing the dies to maintain their performance over extended production runs.
4.Customizability:Cold forging dies can be customized according to specific production requirements. Manufacturers can design dies to produce parts in various shapes and sizes, from simple bolts and nuts to intricate gears and shafts. Custom dies are developed to meet the exact specifications of the client's product, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in production.
Applications
Cold forging dies are used in a wide range of applications, including:
1.Automotive Industry:Manufacturing high-strength fasteners, gears, and shafts for vehicles.
2.Aerospace Industry:Producing lightweight and durable components such as brackets, fittings, and connectors.
3.Construction Industry:Creating high-strength bolts, nuts, and other fasteners for construction projects.
4.Electronics Industry:Fabricating precision connectors and small metal components used in electronic devices.
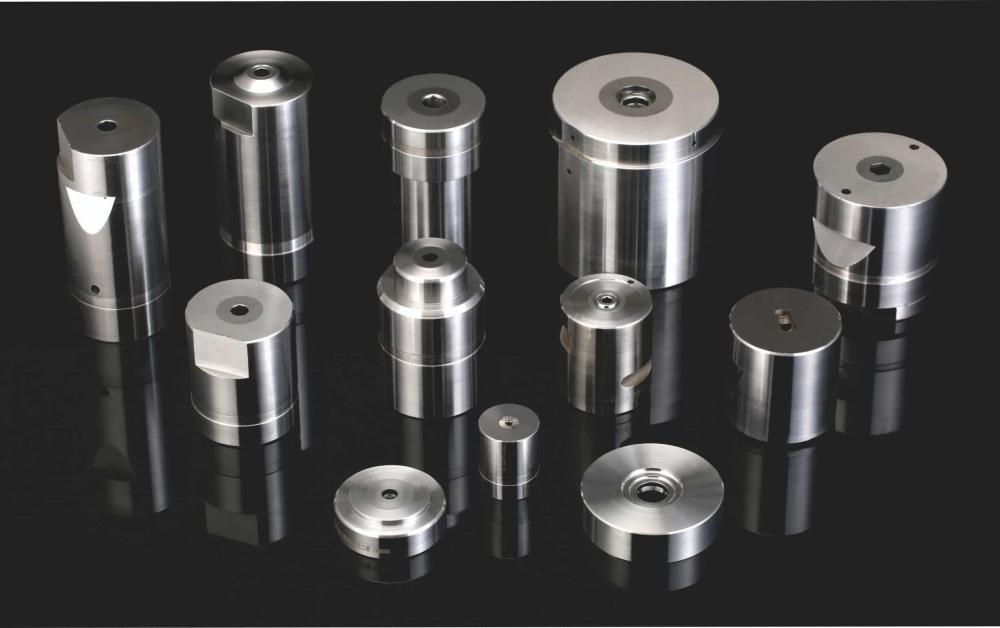

Advantages of Cold Forging Dies
1.High Strength and Durability:The cold forging process increases the strength and toughness of the metal parts produced, making them ideal for applications where high performance and reliability are critical.
2.Cost-Effective Production:Cold forging dies enable mass production of metal components with minimal material waste. The process is highly efficient, reducing production costs while maintaining high quality.
3.Improved Surface Finish:Components produced using cold forging dies often have a superior surface finish, reducing the need for additional machining or finishing processes.
4.Environmental Benefits:Cold forging is an energy-efficient process that requires less energy compared to hot forging, making it a more environmentally friendly manufacturing method.
Quality Assurance
Manufacturers of cold forging dies adhere to strict quality control standards to ensure that the dies meet the highest performance and durability requirements. This includes rigorous testing for hardness, dimensional accuracy, and resistance to wear and fatigue.
Q&A About the Product |
What is a cold forging die, and how does it function in the manufacturing process?
A cold forging die is a specialized tool used to shape metal at room temperature through high-pressure deformation. It functions by applying force to a metal blank, causing it to flow into the desired shape without heating the metal.
What materials are typically used to manufacture cold forging dies, and why?
Cold forging dies are typically made from high-grade tool steels like H13 or SKD61, or carbide. These materials are chosen for their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, which allow them to withstand the intense pressures involved in cold forging.
What are the main advantages of using cold forging dies in production?
The main advantages include high-strength components, cost-effective mass production, superior surface finish, and reduced energy consumption compared to hot forging, making it environmentally friendly.
How does the cold forging process differ from hot forging, particularly regarding the role of the die?
Cold forging is performed at room temperature, which results in stronger, more precise parts. Hot forging, by contrast, involves heating the metal, making it easier to shape but potentially leading to lower precision and strength.
Which industries most commonly use cold forging dies, and for what applications?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics use cold forging dies to manufacture high-strength fasteners, gears, shafts, connectors, and other precision components.
What are the key factors to consider when designing a cold forging die?
Key considerations include material selection, die geometry, tolerance levels, surface finish requirements, and the specific properties of the metal being forged. These factors ensure the die can produce parts that meet exact specifications.
What maintenance practices are necessary to extend the lifespan of cold forging dies?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning, inspecting for wear and damage, applying appropriate surface treatments, and periodically regrinding or replacing worn-out dies to ensure continued precision and performance.
What surface treatments are commonly applied to cold forging dies, and what are their benefits?
Surface treatments like nitriding, PVD coating, and carburizing are applied to enhance hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection, which extends the die's lifespan and improves performance.
Can cold forging dies be customized for specific applications, and if so, how?
Yes, cold forging dies can be customized in terms of material, design, size, and shape to meet specific production requirements. Customization ensures the die can produce parts with the desired dimensions and properties.
What quality control measures are typically applied during the production of cold forging dies?
Quality control measures include rigorous testing for hardness, dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and resistance to wear and fatigue. These measures ensure that the dies meet the highest standards of performance and durability.
Q&A About us |
Q: Are you a factory or a trading company?
A: We are a factory and manufacturer based in Dongguan.
Q:What customizable services do you offer?
A: Material, size, shape, convex and concave marking, coating, laser engraving mark and packing are all customizable.
Q: How can I get a quotation from your company?
A: Please contact us through emails, or fill in the form on our website.
In order to quote you as soon as possible, please offer us : Drawings, Material , Quantity , Surface treatment and other requirements.
Q:What is your payment terms?
A: We accept T/T and Western Union. We accept USD and RMB. If you want to use other payment methods, please feel free to contact us.
Q:What language do you speak?
A: We speak Chinese, English.
Q:Can I visit your company?
A: Any time. You are welcome to visit our factory.

Cold Forging Dies Product Information | |
Product Name | Cold Forging Die |
Brand Name | Donglong |
Place of Origin | Dongguan, Guangdong, China |
Specification | Customized on Request |
Customization | Material, size, shape, convex and concave marking, coating, laser engraving mark and packing are all customizable. |
Product Material | Carbide.ASP23 Vanadis.CPMRTXM4.SKD11SKD61HSSA2M2D2SUJ2.S45C.ect |
Standard | DIN ANSI BS JIS |
Tolerance | ±0.002mm |
Surface Treatment | TiCNTiN,Aitain,Ticrnnitriding Black oxygened Black coating etc available |
Polishness | Close to Ra0.2 Hardness Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Hardness | Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Shaping Mode | Grinding, wire cutting, EDM, cnc machining, cnc turning, cnc Milling |
Application | Machinery Parts and Molds |
Material for Core of Cold Forging Dies | ||||||
Grade | WC+Other | Co | Grain Size | Density | Hardness | TRS |
(±0.5%) | (±0.5%) | (g/cm³) | (HRA)±0.5 | (N/mm²) | ||
KG5 | 88 | 12 | Medium | 14.31 | 88.3 | 340 |
KG6 | 86 | 14 | Medium | 14.12 | 87.3 | 320 |
EA65 | 82 | 18 | Coarse | 13.75 | 85 | 300 |
EA90 | 76 | 24 | Coarse | 13.22 | 82.8 | 270 |
ST6 | 85 | 15 | Coarse | 13.8 | 86 | 270 |
ST7 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.4 | 85.3 | 270 |
VA80 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.58 | 84 | 280 |
VA90 | 78 | 22 | Coarse | 13.39 | 82.5 | 240 |
VA95 | 75 | 25 | Coarse | 13.12 | 81.5 | 220 |
Material for Casing of Cold Forging Dies | |||
Material | Hardness (HRC) | Features | Applications |
H13 | 59-61 | H13 is a chromium molybdenum hot work steel with exceptional hot hardness and abrasion resistance, general hardness, and toughness. | Used for extrusion dies, forging dies, stamping tools, etc. |
SKD11 | 58-61 | SKD11 tool steel has good wear resistance and size ability after heat treatment. | Used for tensile dies, cold extrusion dies, first punch holder, etc. |
SKD61 | 43-53 | SKD61 steel is a high-grade die casting die. It has heat shock resistance, heat deformation resistance, heat fatigue resistance. | Used for heat work dies, cold heading dies, second punch holders. |