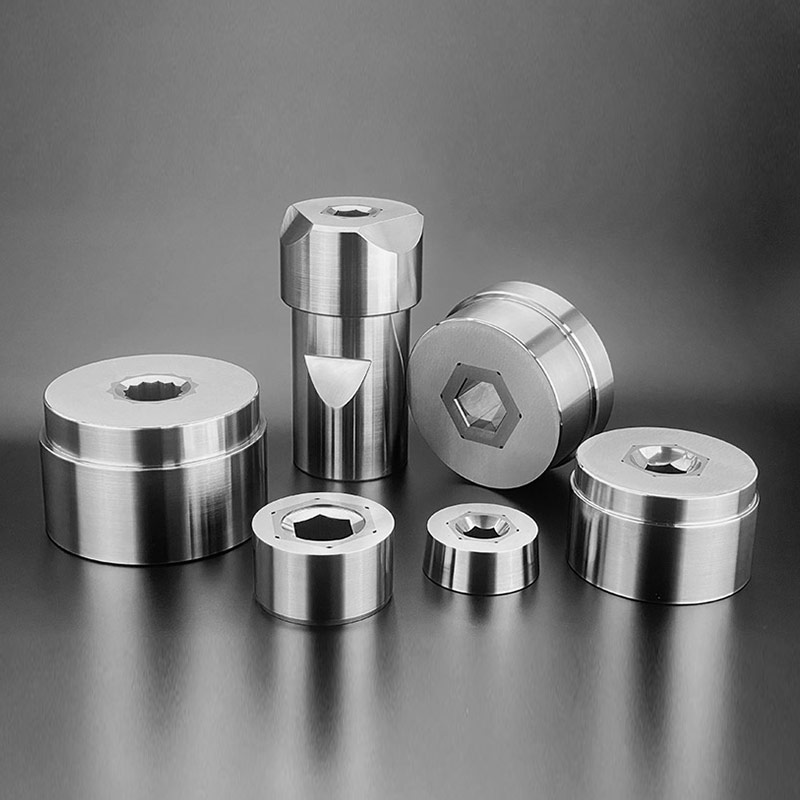
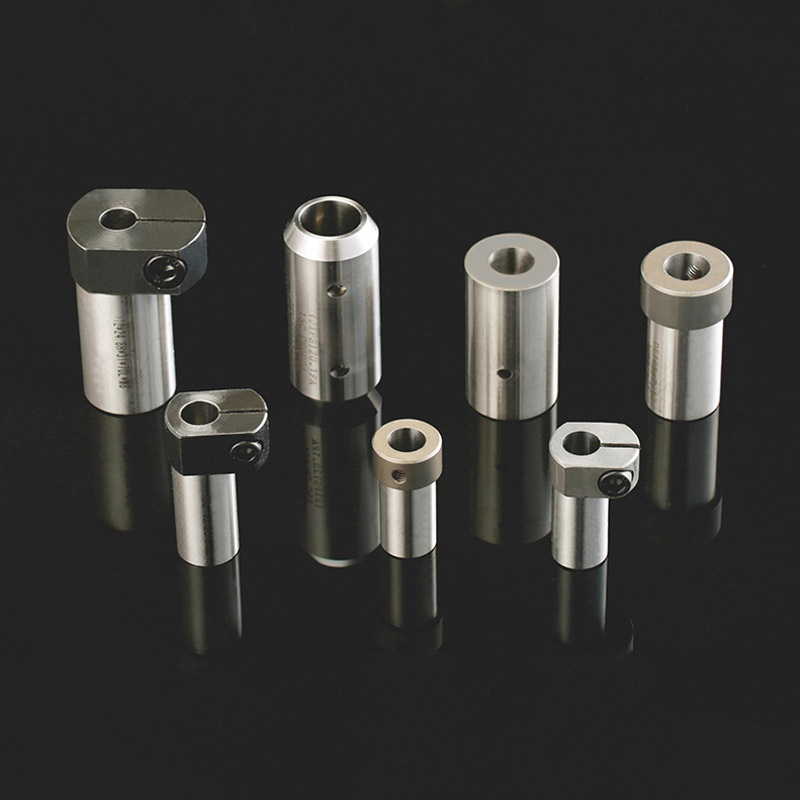
 Tungsten Carbide drawing dies are precision tools used in wire drawing processes. Composed of tungsten carbide, known for its extreme hardness and durability, these dies shape metals into wires or rods of precise diameters. Their superior hardness and wear resistance ensure consistent wire dimensions and surface finishes. With excellent thermal conductivity, they dissipate heat efficiently, prolonging their lifespan. These dies are crucial for producing high-quality wires used in various industries like automotive, electronics, and telecommunications.
Tungsten Carbide drawing dies are precision tools used in wire drawing processes. Composed of tungsten carbide, known for its extreme hardness and durability, these dies shape metals into wires or rods of precise diameters. Their superior hardness and wear resistance ensure consistent wire dimensions and surface finishes. With excellent thermal conductivity, they dissipate heat efficiently, prolonging their lifespan. These dies are crucial for producing high-quality wires used in various industries like automotive, electronics, and telecommunications.
Advantages of Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies
Tungsten Carbide Dies offer several advantages over dies made from other materials:
1.Exceptional Hardness:Tungsten carbide is one of the hardest materials available, making it highly resistant to wear, abrasion, and deformation. This hardness ensures that Tungsten Carbide Dies maintain their shape and dimensional accuracy even after prolonged use.
2.High Wear Resistance:The wear resistance of tungsten carbide means that these dies have a much longer service life compared to steel or other materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing downtime in production.
3.Dimensional Stability:Tungsten carbide dies maintain their dimensional stability under high pressure and temperature, ensuring consistent quality in the parts produced.
4.Corrosion Resistance:Tungsten carbide is resistant to corrosion, which is particularly important in applications involving exposure to harsh environments or corrosive materials.
5.Cost-Effective:Although tungsten carbide dies may have a higher initial cost than other types of dies, their longevity and reduced maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
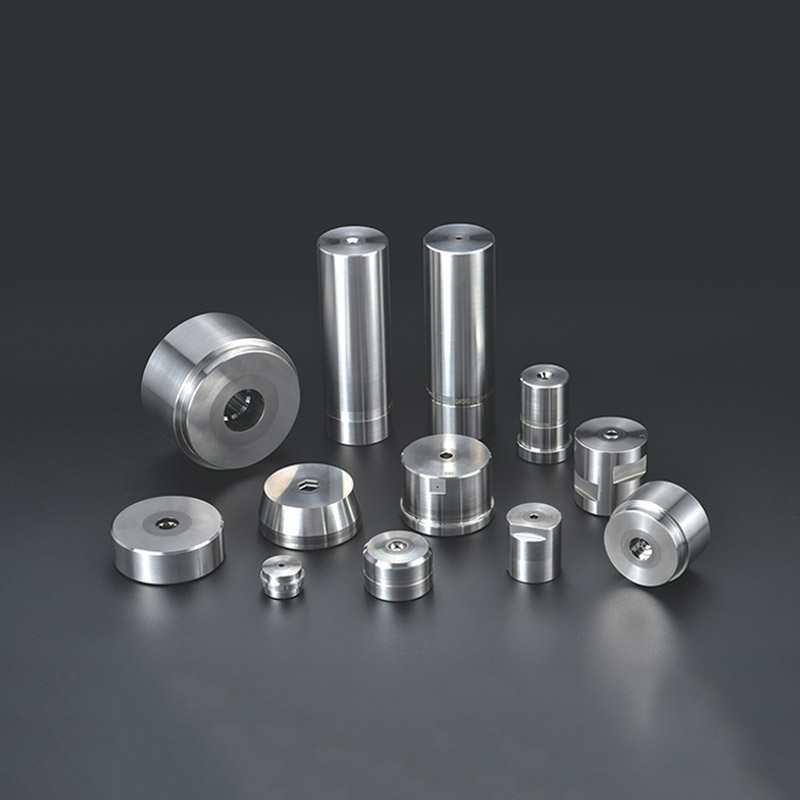
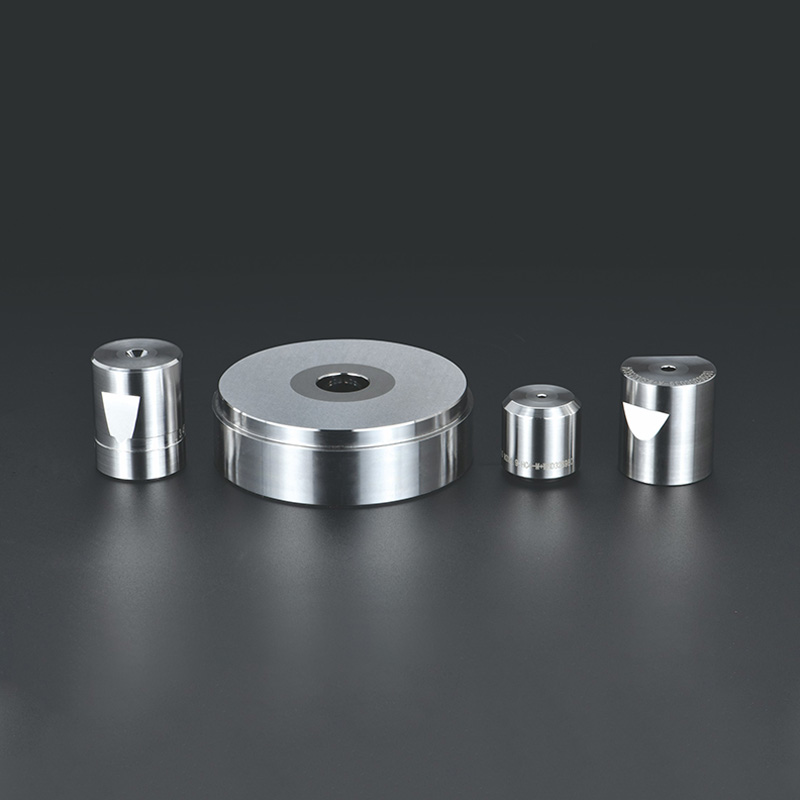


Applications of Tungsten Carbide Dies
Tungsten carbide dies are used in a variety of manufacturing processes, each requiring a specific type of die:
1.Wire Drawing Dies:Tungsten carbide dies are commonly used in wire drawing, where metal rods are pulled through the die to reduce their diameter and increase their length. The hardness and wear resistance of tungsten carbide ensure that the die can handle the high tensile forces and friction involved in this process.
2.Cold Heading Dies:In the cold heading process, metal is formed into a desired shape at room temperature. Tungsten carbide dies are used to create the heads of bolts, screws, and other fasteners, offering the durability needed to withstand repeated impacts without deforming.
3.Extrusion Dies:These dies are used in the extrusion process to force metal through a shaped opening, producing continuous lengths of material with a specific cross-section. Tungsten carbide extrusion dies are essential for producing high-quality, dimensionally accurate components, such as tubes, rods, and profiles.
4.Forming Dies:Tungsten carbide forming dies are used in various metal forming processes, including stamping, bending, and deep drawing. These dies must endure high pressures and maintain their shape over time, making tungsten carbide the material of choice for long-lasting performance.
Challenges in Using Tungsten Carbide Dies
Despite their many advantages, tungsten carbide dies also present some challenges:
1.Brittleness:Tungsten carbide, while extremely hard, can be brittle and prone to cracking under impact or when subjected to sudden shocks. Proper handling and careful use are essential to prevent damage.
2.High Initial Cost:The production of tungsten carbide dies involves complex manufacturing processes and the use of expensive raw materials, leading to a higher initial cost. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
3.Complex Machining:Machining tungsten carbide requires specialized equipment and techniques due to its hardness. This can make the manufacturing process more complex and time-consuming compared to other materials.
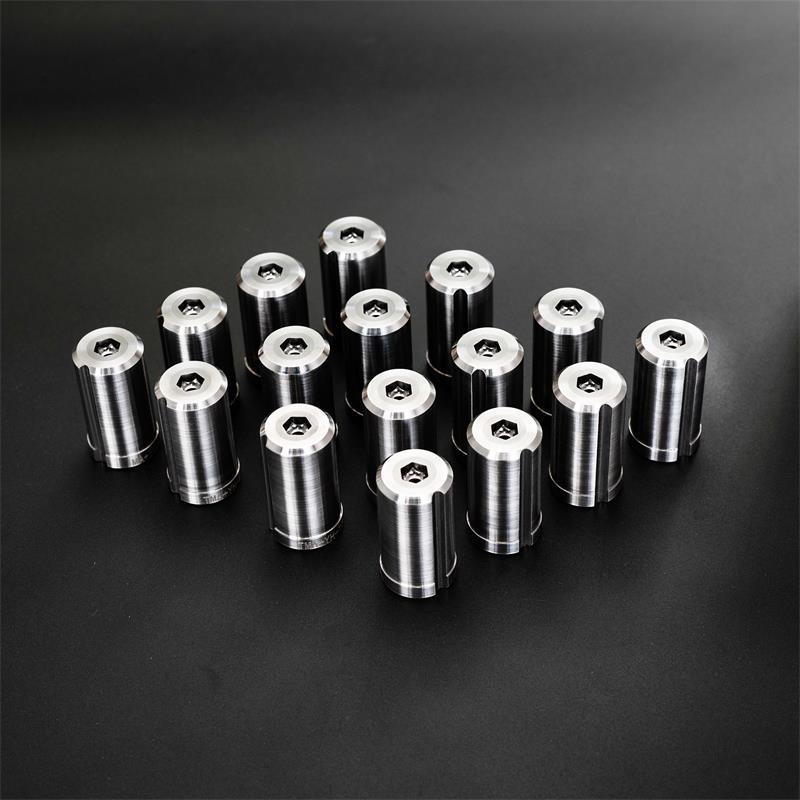


Quality Inspection of Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies
Our tungsten carbide mold quality inspection process includes rigorous checks of dimensional accuracy, surface finish and hardness using Rockwell or Vickers hardness testers. Next, optimum performance is ensured by thoroughly checking concentricity and straightness. Microscopic inspection identifies material defects, while ultrasonic testing detects internal defects. Our rigorous quality control ensures that our tungsten carbide molds meet the highest industry standards for reliability and longevity.
Q&A |
What is Tungsten Carbide Dies?
Tungsten Carbide Dies are molds made of Tungsten Carbide, which are widely used in manufacturing processes due to their extremely high hardness and wear resistance, especially in applications requiring high precision and durability.
What are the main uses of Tungsten Carbide Dies?
Tungsten Carbide Dies are mainly used in wire drawing, cold heading, extrusion molding and other metal working processes, such as the manufacture of bolts, screws, metal tubes and wires.
What are the advantages of Tungsten Carbide Dies over other mold materials?
The main advantages of Tungsten Carbide Dies include its excellent hardness, high wear resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and corrosion resistance, allowing it to maintain its performance over long periods of time.
Are Tungsten Carbide Dies susceptible to damage?
Although Tungsten Carbide Dies are very hard, they are relatively brittle and may break when subjected to severe impacts or sudden jolts, so they need to be handled and used with care.
What is the lifespan of Tungsten Carbide Dies?
Due to its high wear resistance, Tungsten Carbide Dies typically have a longer service life than other mold materials such as Steel Dies, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs.
What are the main challenges of Tungsten Carbide Dies?
The main challenges with Tungsten Carbide Dies include high brittleness and high initial cost. In addition, processing Tungsten Carbide materials requires specialized equipment and techniques, adding to the complexity of manufacturing.
What can I do to improve the service life of Tungsten Carbide Dies?
Regular inspection and maintenance, proper lubrication, avoidance of excessive impacts, and proper operating procedures can help extend the life of Tungsten Carbide Dies.
What industries use Tungsten Carbide Dies?
Tungsten Carbide Dies are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, electronics and heavy machinery industries, especially in the production of parts that require high precision and durability.
Why are Tungsten Carbide Dies expensive to manufacture?
The high cost of manufacturing Tungsten Carbide Dies is mainly due to the expensive raw material of Tungsten Carbide, the difficulty of machining, and the need to use high-precision machining equipment and technology.
How to prevent cracking when using Tungsten Carbide Dies?
In order to prevent Tungsten Carbide Dies from cracking, you should avoid violent impacts, use appropriate processing parameters, and maintain uniform pressure distribution during operation.
As a leading manufacturer of tungsten carbide tooling, we are able to provide cutting-edge solutions for your wire drawing needs, whether you are in the automotive, electronics, or telecommunications industries, our customized tooling is designed to meet your specific application.
At Donglong, customer satisfaction is our top priority. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with tailor-made solutions, offering guidance on mold selection, customization and optimal use. You can contact us at any time for inquiries and consultation, and we look forward to working with you!
Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies Product Information | |
Product Name | Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies |
Brand Name | Donglong |
Place of Origin | Dongguan, Guangdong, China |
Specification | Customized on Request |
Customization | Material, size, shape, convex and concave marking, coating, laser engraving mark and packing are all customizable. |
Product Material | Carbide.ASP23 Vanadis.CPMRTXM4.SKD11SKD61HSSA2M2D2SUJ2.S45C.ect |
Standard | DIN ANSI BS JIS |
Tolerance | ±0.002mm |
Surface Treatment | TiCNTiN,Aitain,Ticrnnitriding Black oxygened Black coating etc available |
Polishness | Close to Ra0.2 Hardness Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Hardness | Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Shaping Mode | Grinding, wire cutting, EDM, cnc machining, cnc turning, cnc Milling |
Application | Machinery Parts and Molds |
Material for Core of Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies | ||||||
Grade | WC+Other | Co | Grain Size | Density | Hardness | TRS |
(±0.5%) | (±0.5%) | (g/cm³) | (HRA)±0.5 | (N/mm²) | ||
KG5 | 88 | 12 | Medium | 14.31 | 88.3 | 340 |
KG6 | 86 | 14 | Medium | 14.12 | 87.3 | 320 |
EA65 | 82 | 18 | Coarse | 13.75 | 85 | 300 |
EA90 | 76 | 24 | Coarse | 13.22 | 82.8 | 270 |
ST6 | 85 | 15 | Coarse | 13.8 | 86 | 270 |
ST7 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.4 | 85.3 | 270 |
VA80 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.58 | 84 | 280 |
VA90 | 78 | 22 | Coarse | 13.39 | 82.5 | 240 |
VA95 | 75 | 25 | Coarse | 13.12 | 81.5 | 220 |
Material for Casing of Tungsten Carbide Drawing Dies | |||
Material | Hardness (HRC) | Features | Applications |
H13 | 59-61 | H13 is a chromium molybdenum hot work steel with exceptional hot hardness and abrasion resistance, general hardness, and toughness. | Used for extrusion dies, forging dies, stamping tools, etc. |
SKD11 | 58-61 | SKD11 tool steel has good wear resistance and size ability after heat treatment. | Used for tensile dies, cold extrusion dies, first punch holder, etc. |
SKD61 | 43-53 | SKD61 steel is a high-grade die casting die. It has heat shock resistance, heat deformation resistance, heat fatigue resistance. | Used for heat work dies, cold heading dies, second punch holders. |