Looking for precision-engineered Bolt Dies that deliver consistent, high-quality threads? Our advanced Bolt Die solutions are crafted to meet the demands of high-volume fastener production and custom threading jobs alike. Whether you're in automotive, aerospace, construction, or general manufacturing, our Bolt Dies are designed to boost productivity and extend tool life—maximizing your return on investment.
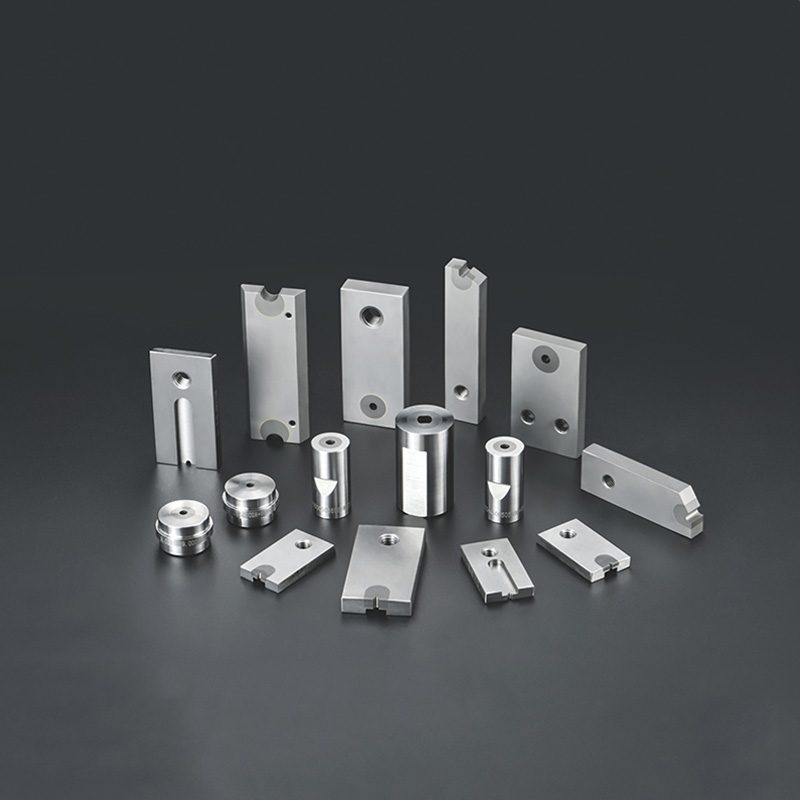

High Thread Precision
Engineered for tight tolerances, our dies ensure every thread meets exact specifications for maximum fit and function.
Extended Tool Life
Made from top-grade materials like HSS, carbide, and cobalt steel, our bolt dies offer exceptional wear resistance, even under high-load conditions.
Application Versatility
From fine pitch threads in aerospace to heavy-duty bolts in construction, our dies support a wide range of thread types and materials.
Customizable Options
We offer OEM/ODM customization to suit specific thread standards (UNC, UNF, Metric) and special design requirements.
The choice of material for bolt dies depends on the specific application. Common materials include:
High-Speed Steel (HSS): Known for its durability and heat resistance, HSS is a popular choice for threading hard metals.
Carbon Steel: Often used for softer materials like mild steel or aluminum, carbon steel dies are affordable but less durable than HSS.
Cobalt Steel: A step up from HSS, cobalt steel offers enhanced hardness and wear resistance, suitable for high-stress threading tasks.
Carbide: Used in high-precision applications, carbide dies are ideal for threading hard or abrasive materials due to their long-lasting cutting edges.
Our bolt dies are trusted across industries:
Automotive: Manufacturing threaded bolts and nuts for assemblies
Aerospace: Producing high-performance fasteners for extreme environments
Construction: Creating secure threaded connections for structural steel
General Manufacturing: Crafting custom-threaded components for tools and equipment
When choosing the right bolt dies for your application, consider these key attributes:
Precision: High-quality dies should produce accurate and consistent threads, ensuring a perfect fit for fasteners.
Durability: The die's material and construction should withstand wear and tear during production.
Ease of Use: Features like adjustability and compatibility with different threading machines enhance production efficiency.
Versatility: Quality dies should accommodate a range of thread sizes and pitches for diverse project needs.
Clean after each use to remove chips and debris
Lubricate regularly to reduce friction and prevent overheating
Store in dry conditions to prevent rust or corrosion
Inspect for wear to ensure consistent threading performance
Selecting the correct bolt die involves several key considerations:
Thread Type: Identify the required thread type (e.g., metric, UNC, UNF) and ensure the die matches the specification.
Material Compatibility: Choose a die that suits the material being threaded, as some dies perform better with specific metals.
Thread Pitch: Ensure the die can handle the required thread pitch for your bolts.
Production Volume: For high-volume production, solid or carbide dies are suitable, while adjustable dies are ideal for smaller, custom batches.
Q: What are bolt dies used for?
A: They are used to form threads on bolts, usually through cold or hot forging processes.
Q: Which materials are best for bolt dies?
A: High-speed steel, cobalt steel, and carbide are commonly used due to their hardness and durability.
Q: Are your bolt dies customizable?
A: Yes, we offer custom designs based on thread type, material, and production requirements.
Q: How long do bolt dies last?
A: With proper maintenance, our bolt dies can endure thousands of cycles in high-volume production environments.
Q: Do you offer bulk pricing or OEM service?
A: Absolutely. We support bulk orders, OEM branding, and global delivery options.
