Cold Heading Mold is a mold specially used for Cold Heading processing. Cold heading is a processing method that stamps metal wires or bars into the desired shape at room temperature. Cold heading is commonly used to produce fasteners such as bolts, screws, rivets, nails, and a variety of other small metal parts. These molds are usually made of high-strength tool steel or carbide materials and undergo precision machining and heat treatment to meet the accuracy and surface quality requirements of the parts and ensure the wear resistance and service life of the mold.
Features of Our Cold Heading Mold
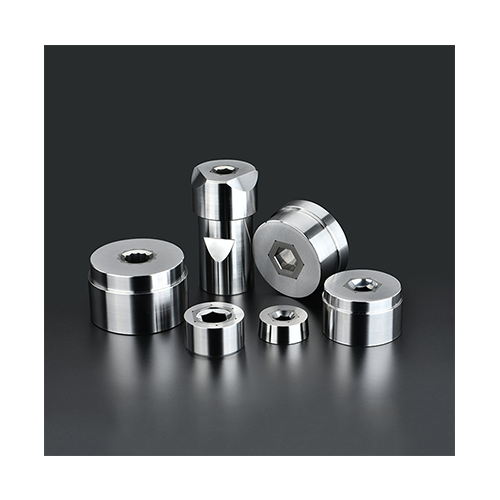

High Precision:Cold heading molds are designed to produce high-precision parts with tight tolerances, crucial for ensuring the final product meets exact specifications.
Durable Materials:Typically made from high-quality tool steels or alloy steels, these molds are engineered to withstand the stresses and strains of the cold heading process, offering long service life.
Customizable Design:Molds can be customized to fit specific part geometries and production requirements. This includes different cavity shapes, sizes, and configurations.
Complex Geometries:Capable of producing complex and intricate shapes, including multi-functional parts like screws and bolts with various head designs and thread forms.
Efficient Cooling Systems:Many cold heading molds incorporate cooling channels to manage the temperature of the mold during operation, which helps maintain consistency and prolongs tool life.
Interchangeable Components:Molds often have interchangeable parts such as punches and dies, allowing for quick changes and adjustments to accommodate different production runs or designs.
High Strength and Toughness:Designed to handle high-pressure forces during the cold heading process, molds must exhibit excellent strength and toughness to avoid deformation or failure.
Wear Resistance:The surfaces of cold heading molds are treated or coated to resist wear and abrasion, which is essential for maintaining mold performance and product quality.
Precision Machining:High-precision machining techniques are used to ensure that all parts of the mold meet exact specifications, contributing to the overall effectiveness and longevity of the mold.
Complex Cooling and Lubrication Systems:Advanced molds may include integrated systems for cooling and lubrication to optimize performance and reduce maintenance needs.
Application Scenarios for Cold Heading Mold
Fastener Industry: Cold heading molds are extensively used in the production of fasteners such as bolts, screws, rivets, and nails. These fasteners are crucial components in industries like construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.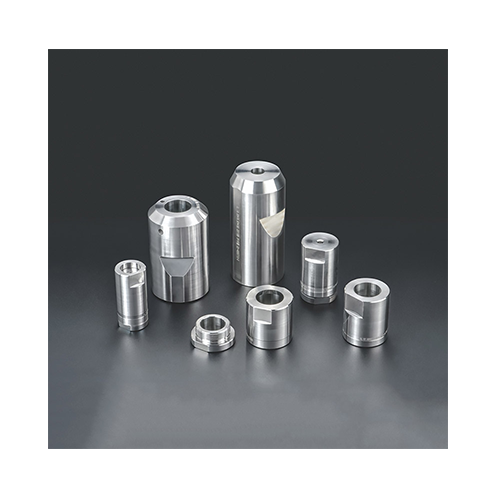
Electronics: Cold heading molds are used to manufacture small metal components used in electronics assembly, such as connectors, terminals, and contacts. These components require high precision and reliability, making cold heading an ideal manufacturing method.
Automotive Industry: Cold heading molds play a significant role in producing various automotive components, including engine parts, transmission components, and chassis fasteners. The automotive industry demands high-quality, durable parts, making cold heading an attractive manufacturing option.
Construction: In the construction industry, cold heading molds are used to produce a wide range of fasteners and structural components, including bolts, anchors, and brackets. These components are essential for building structures and infrastructure projects.
Consumer Goods: Cold heading molds are employed in the production of consumer goods such as appliances, furniture, and sporting goods. They are used to manufacture various metal components, including handles, hinges, and brackets, which require precision and durability.
Medical Devices: Cold heading molds are utilized in the medical device industry to manufacture precision components used in surgical instruments, implants, and medical equipment. Cold heading allows for the production of intricate, high-quality parts with tight tolerances.
Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace and defense applications, cold heading molds are used to produce critical components such as aircraft fasteners, missile parts, and military hardware. These components must meet stringent quality and performance standards, making cold heading an attractive manufacturing method.
| Maintenance Methods for Wire Drawing Dies |
To maintain Wire Drawing Dies, regular cleaning to remove residue and lubrication to minimize friction are essential. Inspection for wear and damage, coupled with proper storage to prevent corrosion, ensures prolonged die life and consistent wire quality. Regular maintenance practices contribute to optimal performance and longevity of Wire Drawing Dies.
| Q&A |
What is a Cold Heading Die?
Cold heading dies are used in the cold heading process, which forms parts by applying pressure to a metal material at room temperature, and are commonly used to produce bolts, nuts and other fasteners.
What are the main components of a cold heading die?
A cold heading die consists of a die body, a punch, a cavity, guide parts and an exhaust system. Each part plays a different role in the cold heading process.
What are the materials used to make cold heading molds?
Common materials include high alloy tool steel, powder metallurgy steel and high hardness alloy materials, which have excellent wear and impact resistance.
What are the main uses of cold heading molds?
Cold heading molds are mainly used to produce various mechanical parts, such as bolts, nuts, nails, pins and so on.
How high is the machining precision of cold heading mold?
The machining accuracy of cold heading mold can reach 0.005mm level, which depends on the design and manufacturing process of the mold.
How long is the life of a cold heading mold?
The life of a cold heading mold is affected by a number of factors, including material quality, operating conditions and maintenance. Typically, a high quality cold heading die will last thousands to tens of thousands of cycles.
How do I maintain and care for my cold heading molds?
Inspect and clean the mold regularly to avoid corrosion and wear. Use proper lubricants and make sure that the temperature and pressure of the tooling is properly controlled during use.
What is the difference between a cold heading die and a hot heading die?
Cold heading dies operate at room temperature, while hot heading dies operate at high temperatures. Cold heading molds are used for metal materials that do not require high temperature heating, while hot heading molds are used for materials that require high temperature deformation.
What are the factors to consider when designing a cold heading mold?
When designing a cold heading mold, you need to consider the fluidity of the material, the cooling system of the mold, the strength and rigidity of the mold, the productivity and the accuracy of the part.
What are the common failures of cold heading molds?
Common failures include wear, cracks, distortion, and galling. Regular maintenance and inspection can effectively minimize the occurrence of these problems.

Cold Heading Mold Product Information | |
Product Name | Cold Heading Mold |
Brand Name | Donglong |
Place of Origin | Dongguan, Guangdong, China |
Specification | Customized on Request |
Customization | Material, size, shape, convex and concave marking, coating, laser engraving mark and packing are all customizable. |
Product Material | Carbide.ASP23 Vanadis.CPMRTXM4.SKD11SKD61HSSA2M2D2SUJ2.S45C.ect |
Standard | DIN ANSI BS JIS |
Tolerance | ±0.002mm |
Surface Treatment | TiCNTiN,Aitain,Ticrnnitriding Black oxygened Black coating etc available |
Polishness | Close to Ra0.2 Hardness Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Hardness | Depends on material(HRC60~94) |
Shaping Mode | Grinding, wire cutting, EDM, cnc machining, cnc turning, cnc Milling |
Application | Machinery Parts and Molds |
Material for Core of Wire Drawing Dies | ||||||
Grade | WC+Other | Co | Grain Size | Density | Hardness | TRS |
(±0.5%) | (±0.5%) | (g/cm³) | (HRA)±0.5 | (N/mm²) | ||
KG5 | 88 | 12 | Medium | 14.31 | 88.3 | 340 |
KG6 | 86 | 14 | Medium | 14.12 | 87.3 | 320 |
EA65 | 82 | 18 | Coarse | 13.75 | 85 | 300 |
EA90 | 76 | 24 | Coarse | 13.22 | 82.8 | 270 |
ST6 | 85 | 15 | Coarse | 13.8 | 86 | 270 |
ST7 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.4 | 85.3 | 270 |
VA80 | 80 | 20 | Coarse | 13.58 | 84 | 280 |
VA90 | 78 | 22 | Coarse | 13.39 | 82.5 | 240 |
VA95 | 75 | 25 | Coarse | 13.12 | 81.5 | 220 |
Material for Casing of Cold Heading Mold | |||
Material | Hardness (HRC) | Features | Applications |
H13 | 59-61 | H13 is a chromium molybdenum hot work steel with exceptional hot hardness and abrasion resistance, general hardness, and toughness. | Used for extrusion dies, forging dies, stamping tools, etc. |
SKD11 | 58-61 | SKD11 tool steel has good wear resistance and size ability after heat treatment. | Used for tensile dies, cold extrusion dies, first punch holder, etc. |
SKD61 | 43-53 | SKD61 steel is a high-grade die casting die. It has heat shock resistance, heat deformation resistance, heat fatigue resistance. | Used for heat work dies, cold heading dies, second punch holders. |