Fastener Dies play a crucial role in the production of bolts, nuts, screws, and other fasteners. The quality of Fastener Dies directly affects the precision, strength, and durability of fasteners. Producing high-quality and long-lasting fastener dies requires adherence to a series of precise manufacturing processes. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the key manufacturing processes involved in fastener die production.
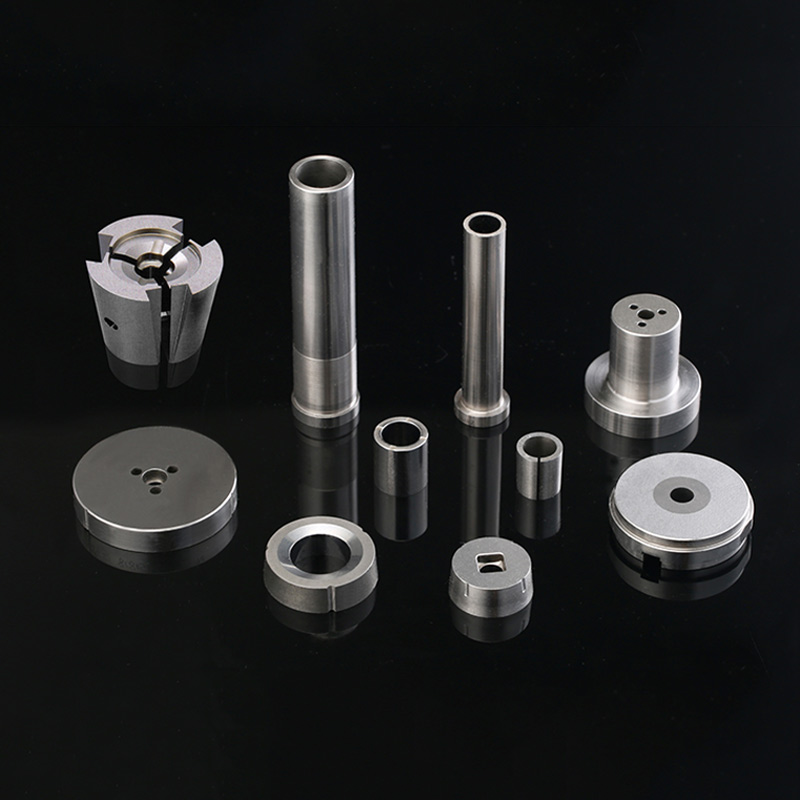

1. Material Selection and Pre-Treatment
The first step in manufacturing fastener dies is selecting the right material, which determines the die’s durability, wear resistance, and performance. Common materials include:
Tungsten Carbide – Exceptional hardness and wear resistance, ideal for high-strength fastener dies.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) – Offers a balance of hardness and toughness, suitable for most Cold Heading and extrusion dies.
Alloy Tool Steel (e.g., D2, SKD11, H13) – Provides good wear resistance and impact resistance, making it suitable for various fastener forming applications.
Once the material is selected, it often undergoes forging or heat treatment pre-processing to improve its microstructure, reduce internal stress, and enhance the die’s overall lifespan.
2. Precision Machining Techniques
Precision machining is at the core of fastener die production, ensuring accurate dimensions, tight tolerances, and high surface finish quality. Key machining techniques include:
(1) CNC Turning and Milling
CNC turning is used to shape the basic form of the die, ensuring precise dimensions.
CNC milling processes intricate features such as grooves and screw threads, enhancing production efficiency and consistency.
(2) Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Ideal for complex die shapes, such as thread-forming dies and hexagonal nut dies.
EDM removes material through electrical discharge, allowing for high-precision detailing on hardened metals.
(3) Wire EDM
Used to cut precise profiles, such as internal holes and complex contours.
Wire EDM provides extremely high accuracy, with tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm.
3. Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
Fastener dies must withstand high-pressure operations, requiring excellent wear resistance, impact resistance, and thermal stability. Heat treatment and surface hardening processes are essential for improving the die’s lifespan.
(1) Hardening and Tempering
Techniques such as vacuum hardening, salt bath hardening, and induction hardening increase die hardness and wear resistance.
Tempering ensures that the die retains both hardness and toughness, preventing brittle fractures.
(2) Surface Coating (PVD / CVD)
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coatings, such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) and TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), improve wear resistance and oxidation resistance.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) is used for high-temperature applications, enhancing heat resistance and corrosion protection.
(3) Ultra-Fine Polishing and Deburring
Manual, ultrasonic, or electrochemical polishing reduces surface roughness, ensuring superior fastener quality.
Deburring ensures smooth edges, minimizing material wear during fastener production.
4. Quality Inspection and Assembly Testing
Before being deployed in fastener production, dies undergo strict quality inspection and trial runs to ensure precision and durability.
(1) Dimensional and Precision Inspection
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) verify critical dimensions and tolerances.
Hardness testing ensures the die meets required hardness specifications.
(2) Trial Runs and Optimization
Dies are tested in cold heading machines to assess their forming performance.
If necessary, adjustments such as secondary grinding or surface refinements are made to enhance precision and longevity.
5. Die Maintenance and Reconditioning
To extend the lifespan of fastener dies, manufacturers implement regular maintenance and reconditioning processes.
Die repair – Minor refinements, polishing, and size adjustments help restore precision.
Recoating – Worn-out coatings can be reapplied using PVD to enhance durability.
Re-machining – Slightly worn dies can undergo precision grinding or EDM touch-ups to extend their usability.
Fastener die production involves a complex set of processes, including material selection, precision machining, heat treatment, surface coating, and stringent quality control. High-quality fastener dies not only improve production efficiency but also reduce costs and enhance the overall quality of fasteners. As CNC machining and surface treatment technologies continue to evolve, the manufacturing of fastener dies is becoming more advanced, meeting the growing demands of various industries.