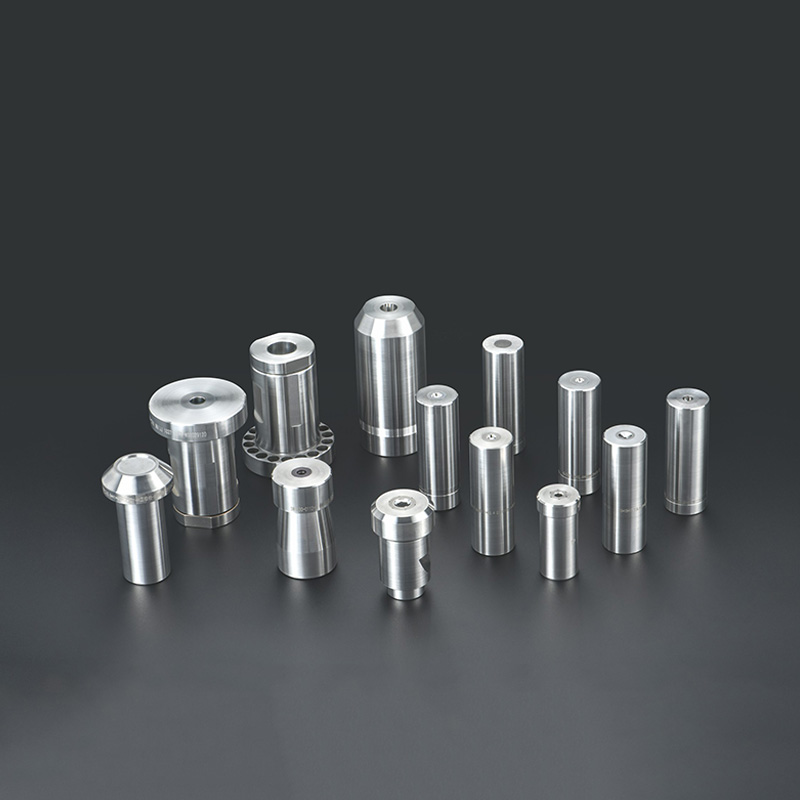
Cold Heading Die, an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing, is widely used in the production of fasteners such as bolts, nuts, and rivets. By utilizing Cold Heading processes to plastically deform metal materials at room temperature, it not only enhances production efficiency but also significantly reduces material waste. This article explores the technical principles, market status, application areas, and future trends of Cold Heading Die, providing valuable insights for industry professionals.

Technical Principles and Innovations of Cold Heading Die
The core technology of Cold Heading Die lies in its ability to achieve high-precision plastic deformation of metal materials at room temperature. The dies are typically made of high-hardness alloy steels, such as 302HQ, 304HC, and 316, to ensure wear resistance and longevity. The cold heading process involves continuous operations using multi-station dies to gradually shape metal wire into the desired fastener form.
Compared to traditional hot heading processes, Cold Heading Die offers the following advantages:
High Efficiency: The cold heading process eliminates the need for heating, reducing energy consumption and production cycles.
High Precision: Die design ensures consistent product dimensions, meeting high-precision requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced material waste and fewer post-processing steps lower production costs.
Market Status and Development Trends of Cold Heading Die
Globally, Cold Heading Die technology is well-established in Europe and the United States, particularly in the automotive and electronics industries. According to the ISO 4954:2021 standard, the physical and mechanical properties of cold heading and cold extrusion steels are strictly regulated, further driving the advancement of Cold Heading Die technology.
In China, the adoption rate of Cold Heading Die technology is increasing annually. In 2023, China's precision mold market reached 18.2 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 9.3%. By 2025, with the advancement of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, the Cold Heading Die market is expected to experience significant growth.
Application Areas and Case Studies of Cold Heading Die
Cold Heading Die is widely used in the following fields:
Automotive Manufacturing: Producing high-strength bolts, nuts, and other fasteners to meet lightweight and safety requirements.
Electronics Industry: Ensuring high precision and consistency in the production of precision electronic components.
Construction Industry: Manufacturing rivets and anchor bolts to improve construction efficiency and quality.
For example, a leading automotive parts manufacturer adopted Cold Heading Die technology and achieved a 25% increase in production efficiency and a 15% reduction in defect rates, significantly enhancing its market competitiveness.
Future Prospects of Cold Heading Die
As manufacturing moves toward intelligence and sustainability, Cold Heading Die technology will witness more innovative opportunities:
Intelligence: Integration of sensors and control systems for real-time monitoring and automatic adjustments.
Green Manufacturing: Using eco-friendly materials and energy-saving technologies to reduce energy consumption and pollution.
Multifunctionality: Combining cold heading with functions like heat treatment and surface treatment to meet diverse production needs.
As a vital component of modern manufacturing, Cold Heading Die technology is driving the industry toward greater efficiency, precision, and intelligence. With continuous technological advancements and growing market demand, Cold Heading Die will unlock its unique potential in more fields, injecting new vitality into the transformation and upgrading of manufacturing. In the future, companies should seize this technological opportunity, increase R&D investment, and enhance their core competitiveness to thrive in an increasingly competitive market.