What is a Cold Heading Mold?
Cold Heading molds are precision tooling components used in cold heading processes to form metal parts at room temperature through plastic deformation. These molds are typically made from high-grade tool steels (e.g., M2, M35, or Tungsten Carbide with 90-94% WC content) and undergo specialized heat treatment to achieve surface hardness of 60-65 HRC with core toughness of 45-50 HRC. The molds feature dimensional tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm for critical forming zones and surface finishes better than Ra 0.2μm to minimize friction during material flow.
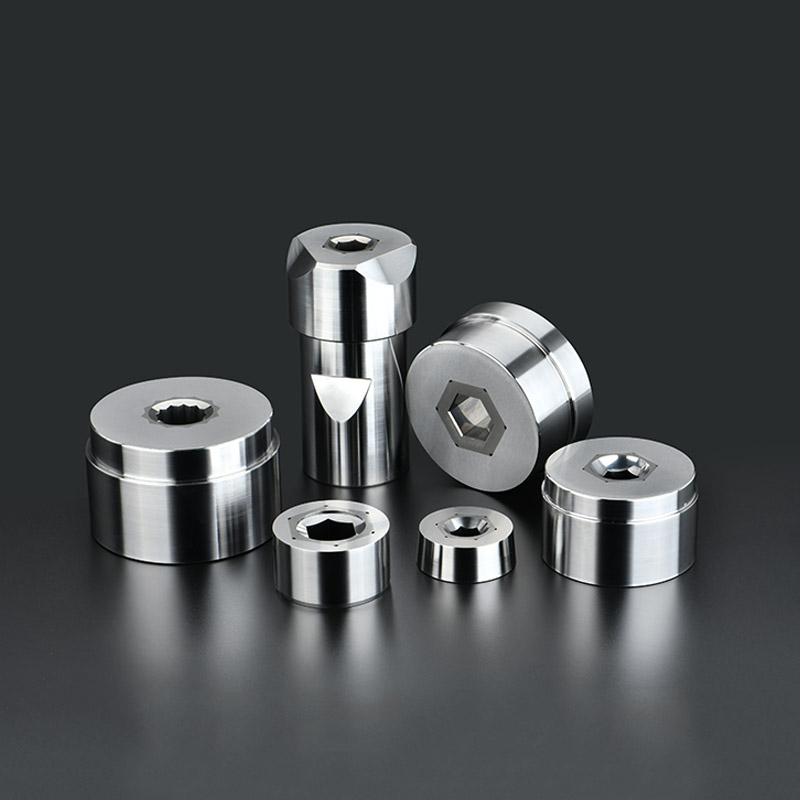

Key characteristics of Cold Heading Molds include:
High Wear Resistance: Achieved through surface treatments like TiN coating (3-5μm thickness) or cryogenic processing, extending tool life by 300-500% compared to untreated tools
Precision Geometry: Punch noses maintain radii within ±0.01mm tolerance, while die cavities maintain concentricity under 0.003mm TIR
Fatigue Resistance: Designed to withstand >1 million cycles at forming pressures up to 2500 MPa without cracking
Thermal Stability: Maintain dimensional stability within 0.002mm/°C during operation despite frictional heating
Applications of Cold Heading Molds
Cold heading molds serve critical functions across multiple industries:
Fastener Manufacturing
Produce high-volume fasteners with production rates reaching 400-600 pieces/minute for standard bolts and nuts. Specialized molds create:
Hex head bolts with M3-M24 thread sizes
Shoulder bolts with diameter transitions within 0.05mm concentricity
Torx screws with 6-lobe profiles maintaining ±0.025mm form tolerance
Automotive Components
Form precision parts meeting ISO/TS 16949 standards:
Valve retainers with 0.01mm runout requirements
Wheel studs with 10.9 grade tensile strength
Fuel injector components with surface finishes <0.4μm Ra
Electronics Hardware
Create miniature components with:
Micro-screws down to M0.6 size
Connector pins with 0.3mm diameter tolerances
Shielding contacts requiring <0.005mm burr heights
Aerospace Fasteners
Manufacture high-strength components meeting NASM/ASME specifications:
Hi-lok collars with 160 ksi shear strength
Titanium fasteners formed at 45-50% reduction ratios
Flush head rivets with 100° countersink angles
Maintenance Procedures for Cold Heading Molds
Daily Maintenance
Clean forming surfaces every 4-8 hours using ultrasonic cleaners with pH-neutral solutions
Inspect punch tips for wear exceeding 0.02mm radius increase
Apply dry-film lubricants (MoS2-based) with 5-10μm coating thickness
Preventive Maintenance
Measure die concentricity weekly using 0.001mm resolution dial indicators
Perform hardness testing every 50,000 cycles to detect softening below 58 HRC
Polish forming surfaces with 0.3μm diamond paste when surface roughness exceeds Ra 0.5μm
Storage Procedures
Store in climate-controlled environments (20±2°C, 40-50% RH)
Use VCI paper with 0.05mm thickness for corrosion protection
Mount molds vertically with 10mm rubber isolators between tools
Repair Techniques
Re-grind punch noses using 46-grit CBN wheels at 25 m/s surface speed
Apply laser cladding for die repairs with 0.1mm layer precision
Re-coat tools when coating wear exceeds 30% of original thickness