Hot Heading Dies are a type of mold used in the hot heading process. Hot heading is a method of manufacturing metal parts by heating the metal to a specific temperature and then applying pressure to it using a die to form it into the desired shape.Hot Heading Dies are usually made of high-temperature-resistant die steel or carbide materials to withstand high temperatures and strong impacts.
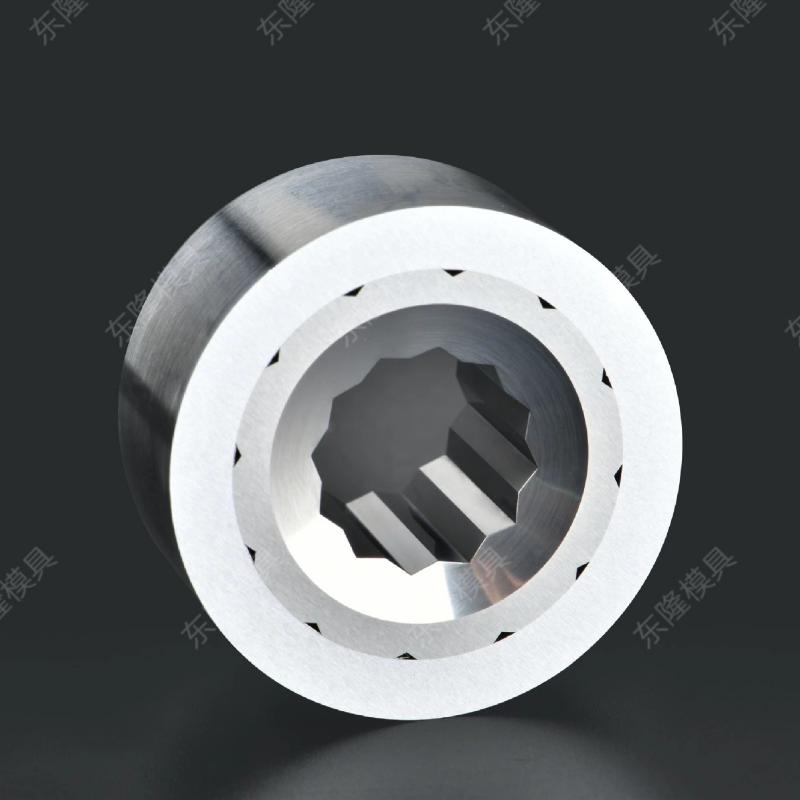

Application areas for Hot Heading Dies
Hot Heading Dies are used in a wide range of industries, especially in the manufacture of fasteners, bolts, screws, rivets, automotive parts and aerospace parts. In these areas, precision and strength are critical, so the use of quality molds is essential to ensure product quality.
Manufacturing Process for Hot Heading Dies
Manufacturing Hot Heading Dies requires a multi-step precision process that includes:
1. Material Selection: Tool steel or Tungsten Carbide, a high-strength, wear-resistant material, is typically chosen for the mold material.
2. Machining steps: The machining process includes CNC milling, grinding, heat treatment and surface coating treatment.
3. Heat treatment: Heat treatment improves the hardness and wear resistance of the mold to ensure that the mold can be used for a long time at high temperatures.
Design Features of Hot Heading Dies
The design of Hot Heading Dies usually includes the following key factors:
1. Die Shape and Accuracy: The shape of the die must be precise to ensure that the metal is formed evenly during the hot heading process.
2. Heat Resistance: Because they operate at high temperatures, dies must be able to withstand high temperatures and maintain a stable shape.
3. Life and Durability: Hot Heading Dies need to have a long life in order to reduce the cost of frequent tooling changes. 5.
Advantages of Hot Heading Dies
The Hot Heading process offers the following advantages over the Cold Heading process through the use of Hot Heading Dies:
1. Better material ductility: Metals deform more easily when heated, allowing for more complex shapes to be created.
2. Reduced Stress Concentration: The stresses in the metal are more evenly distributed during the Hot Heading process, which helps to increase the strength and durability of the part.
3. Higher productivity: Due to the lower resistance to deformation of the metal after heating, productivity is usually higher.
Common Hot Heading Dies Problems and Solutions
1. Wear and tear: Molds are prone to wear and tear due to high temperatures and pressures. The wear resistance of the mold can be improved by surface coating treatment (e.g. PVD or CVD coating).
2. Cracking: Improper heat treatment may cause the mold to crack during use. Ensuring proper heat treatment and mold design can reduce this problem.